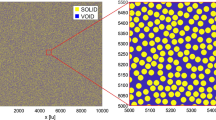
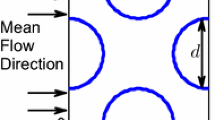
Abstract
We consider flow and upscaling of flow properties from pore scale to Darcy scale, when the pore-scale geometry is changing. The idea is to avoid having to solve for the pore evolution at the pore scale, because this results in unmanageable complexity. We propose to use stochastic modeling to parametrize plausible modifications of the pore geometry and to construct distributions of permeability parametrized by Darcy-scale variables. To localize the effects of, e.g., clogging, we introduce an intermediate scale of pore-network models. We use local Stokes solvers to calibrate the throat permeability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angot, P.: Analysis of singular perturbations on the Brinkman problem for fictitious domain models of viscous flows. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 22(16), 1395–1412 (1999)
Angot, P., Bruneau, C.H., Fabrie, P.: A penalization method to take into account obstacles in incompressible viscous flows. Numer. Math. 81(4), 497–520 (1999)
Arbogast, T., Brunson, D.S.: A computational method for approximating a Darcy-Stokes system governing a vuggy porous medium. Comput. Geosci. 11(3), 207 (2007)
Arbogast, T., Lehr, H.L.: Homogenization of a Darcy–Stokes system modeling vuggy porous media. Comput. Geosci. 10(3), 291–302 (2006)
Auriault, J.L.: On the domain of validity of Brinkman’s equation. Transp. Porous Media 79(2), 215–223 (2009)
Balhoff, M.T., Thomas, S.G., Wheeler, M.F.: Mortar coupling and upscaling of pore-scale models. Comput. Geosci. 12(1), 15–27 (2008)
Bear, J.: Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media. Dover, New York (1972)
Bear, J., Cheng, A.D.: Modeling Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport, vol. 23. Springer Science & Business Media (2010)
Blunt, M.J.: Flow in porous media–pore-network models and multiphase flow. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 6(3), 197–207 (2001)
Boffi, D., Brezzi, F., Fortin, M., et al.: Mixed Finite Element Methods and Applications, vol. 44. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Bringedal, C., Berre, I., Pop, I.S., Radu, F.A.: A model for non-isothermal flow and mineral precipitation and dissolution in a thin strip. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 289, 346–355 (2015)
Cai, R., Lindquist, W.B., Um, W., Jones, K.W.: Tomographic analysis of reactive flow induced pore structure changes in column experiments. Adv. Water Resour. 32(9), 1396–1403 (2009)
Canuto, C., Kozubek, T.: A fictitious domain approach to the numerical solution of PDEs in stochastic domains. Numer. Math. 107(2), 257–293 (2007)
Cesmelioglu, A., Girault, V., Riviere, B.: Time-dependent coupling of Navier–Stokes and Darcy flows. ESAIM: Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 47(2), 539–554 (2013)
Chu, J., Engquist, B., Prodanovic, M., Tsai, R.: A multiscale method coupling network and continuum models in porous media i: steady-state single phase flow. Multiscale Model. Simul. 10(2), 515–549 (2012)
Costa, T.B.: Hybrid multiscale methods with applications to semiconductors, porous media, and materials science. Ph.D. thesis (2016)
Costa, T.B.: HybGe-Flow3D v2.0.0. https://github.com/numsol/HybGe-Flow3D (2017)
Crandell, L., Peters, C.A., Um, W., Jones, K.W., Lindquist, W.B.: Changes in the pore network structure of hanford sediment after reaction with caustic tank wastes. J. Contam. Hydrol. 131(1), 89–99 (2012)
Dong, H., Blunt, M.J.: Pore-network extraction from micro-computerized-tomography images. Physical Rev. E 80(3), 036307 (2009)
Ern, A., Guermond, J.L.: Theory and Practice of Finite Elements, vol. 159. Springer Science & Business Media, New York (2013)
Eymard, R., Gallouët, T., Herbin, R.: Finite volume methods. Handb. Numer. Anal. 7, 713–1018 (2000)
Gibson, N.L., Medina, F.P., Peszynska, M., Showalter, R.E.: Evolution of phase transitions in methane hydrate. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 409(2), 816–833 (2014)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Approximation of the Navier-Stokes Equations(book) (Lecture Notes in Mathematics), vol. 749. Springer, Berlin (1979)
Gordon, A., Powell, C.E.: A preconditioner for fictitious domain formulations of elliptic PDEs on uncertain parameterized domains. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2(1), 622–646 (2014)
Harbrecht, H., Peters, M.: Combination technique based second moment analysis for PDEs on random domains. In: Sparse Grids and Applications - Stuttgart, pp 51–77. Springer, Cham (2014)
Harbrecht, H., Peters, M., Siebenmorgen, M.: Numerical solution of elliptic diffusion problems on random domains. Preprint 2014-08, Mathematisches Institut, Universität Basel (2014)
Hassanizadeh, M., Gray, W.G.: General conservation equations for multi-phase systems: 1. Averaging procedure. Adv. Water Resour. 2, 131–144 (1979)
Hassanizadeh, M., Gray, W.G.: General conservation equations for multi-phase systems: 2. Mass, momenta, energy, and entropy equations. Adv. Water Resour. 2, 191–203 (1979)
Hornung, U.: Homogenization and Porous Media, vol. 6. Springer Science & Business Media, New Year (2012)
Kim, D., Peters, C., Lindquist, W.: Upscaling geochemical reaction rates accompanying acidic CO2-saturated brine flow in sandstone aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 47(1) (2011)
Krotkiewski, M., Ligaarden, I.S., Lie, K.A., Schmid, D.W.: On the importance of the Stokes-Brinkman equations for computing effective permeability in karst reservoirs. Commun. Comput. Phys. 10(05), 1315–1332 (2011)
Labs, P.: Paralution v1.0.0. http://www.paralution.com/ (2015)
Lindquist, W.B., Lee, S., Oh, W., Venkatarangan, A., Shin, H., Prodanovic, M.: 3DMA-Rock: a software package for automated analysis of rock pore structure in 3-D computed microtomography images. SUNY Stony Brook (2005)
Lukarski, M.S.D.: Parallel sparse linear algebra for multi-core and many-core platforms. Ph.D. thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology (2012)
Mahabadi, N., Dai, S., Seol, Y., Sup Yun, T., Jang, J.: The water retention curve and relative permeability for gas production from hydrate-bearing sediments: pore-network model simulation. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 17(8), 3099–3110 (2016)
Medina, F.P., Peszynska, M.: Hybrid modeling and analysis of multicomponent adsorption with applications to coalbed methane. In: Wolfe, D. (ed.) Porous Media: Theory, Properties, and Applications, chapter 1, pp 1–52. Nova, Commack (2016)
Mikelic, A., Jäger, W.: On the interface boundary condition of Beavers, Joseph, and Saffman. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 60(4), 1111–1127 (2000)
Mittal, R., Iaccarino, G.: Immersed boundary methods. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 37, 239–261 (2005)
Ossiander, M., Peszynska, M., Vasylkivska, V.: Conditional Stochastic Simulations of Flow and Transport with Karhunen-Loeve Expansions, Stochastic Collocation, and Sequential Gaussian Simulation. J. Appl. Math. 2014 (652594), 21 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/652594
Ossiander, M., Peszynska, M., Madsen, L., Mur, A., Harbert, W.: Estimation and simulation for geospatial porosity and permeability data. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 24, 109 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10651-016-0362-y
Patankar, S.: Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1980)
Peskin, C.S.: The immersed boundary method. Acta Numer. 11, 479–517 (2002)
Peszyńska, M., Wheeler, M.F., Yotov, I.: Mortar upscaling for multiphase flow in porous media. Comput. Geosci. 6(1), 73–100 (2002)
Peszyńska, M., Trykozko, A., Augustson, K.: Computational upscaling of inertia effects from porescale to mesoscale, pp 695–704. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Peszynska, M., Trykozko, A.: Convergence and Stability in Upscaling of Flow with Inertia from Porescale to Mesoscale. Int. J. Multiscale Comput. Eng. 9(2), 215–229 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJMultCompEng.v9.i2.60
Peszynska, M., Trykozko, A.: Pore-to-core simulations of flow with large velocities using continuum models and imaging data. Comput. Geosci. 17(4), 623–645 (2013)
Peszynska, M., Trykozko, A., Iltis, G., Schlueter, S., Wildenschild, D.: Biofilm growth in porous media: experiments, computational modeling at the porescale, and upscaling. Adv. Water Resour. 95, 288–301 (2016)
Prodanović, M., Lindquist, W., Seright, R.: 3D image-based characterization of fluid displacement in a Berea core. Adv. Water Resour. 30(2), 214–226 (2007)
Pruess, K., Garcia, J.: Multiphase flow dynamics during CO2 disposal into saline aquifers. Environ. Geol. 42(2), 282–295 (2002)
Quarteroni, A., Valli, A.: Domain Decomposition Methods for Partial Differential Equations. CMCS-BOOK-2009-019. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1999)
Quarteroni, A., Manzoni, A., Negri, F.: Reduced Basis Methods for Partial Differential Equations: an Introduction, vol. 92. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Raoof, A., Hassanizadeh, S.M., Leijnse, A.: Upscaling transport of adsorbing solutes in porous media: pore-network modeling. Vadose Zone J. 9(3), 624–636 (2010)
Raoof, A., Nick, H., Hassanizadeh, S., Spiers, C.: Poreflow: a complex pore-network model for simulation of reactive transport in variably saturated porous media. Comput. Geosci. 61, 160–174 (2013)
Russell, T.F., Wheeler, M.F.: Finite element and finite difference methods for continuous flows in porous media. In: The Mathematics of Reservoir Simulation, vol. 1, pp 35–106 (1983)
Sánchez-Palencia, E.: Non-homogeneous media and vibration theory. In: Non-homogeneous Media and Vibration Theory, vol. 127 (1980)
Schulz, R., Ray, N., Frank, F., Mahato, H., Knabner, P.: Strong solvability up to clogging of an effective diffusion–precipitation model in an evolving porous medium. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 28(2), 179–207 (2017)
Silin, D., Patzek, T.: Pore space morphology analysis using maximal inscribed spheres. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 371(2), 336–360 (2006)
Spiteri, E., Juanes, R., Blunt, M.J., Orr, F.M., et al.: Relative-permeability hysteresis: trapping models and application to geological CO2 sequestration. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers (2005)
Tartar, L.: Convergence of the homogenization process. In: Nonhomogeneous Media and Vibration Theory (1980)
Trykozko, A., Brouwer, G., Zijl, W.: Downscaling: a complement to homogenization. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 5, 157–170 (2008)
Trykozko, A., Zijl, W., Bossavit, A.: Nodal and mixed finite elements for the numerical homogenization of 3D permeability. Comput. Geosci. 5(1), 61–84 (2001)
van Noorden, T.L., Pop, I., Ebigbo, A., Helmig, R.: An upscaled model for biofilm growth in a thin strip. Water Resour. Res. 46(6) (2010)
Versteeg, H.K., Malalasekera, W.: An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: the Finite Volume Method. Pearson Education (2007)
Vo, H.X., Durlofsky, L.J.: A new differentiable parameterization based on principal component analysis for the low-dimensional representation of complex geological models. Math. Geosci. 46(7), 775–813 (2014)
Weinan, E., Engquist, B., Li, X., Ren, W., Vanden-Eijnden, E.: Heterogeneous multiscale methods: a review. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2(3), 367–450 (2007)
Whitaker, S.: Volume averaging of transport equations. In: Prieur du Plessis, J (ed.) Fluid Transport in Porous Media. Computational Mechanics Publications, Southampton (1997)
Xiu, D.: Numerical Methods for Stochastic Computations: a Spectral Method Approach. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2010)
Xiu, D., Tartakovsky, D.M.: Numerical methods for differential equations in random domains. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 28(3), 1167–1185 (2006)
Zijl, W., Trykozko, A.: Numerical homogenization of the absolute permeability using the conformal-nodal and mixed-hybrid finite element method. Transp. Porous Media 44(1), 33–62 (2001)
Acknowledgements
Wewould like to gratefully acknowledge the collaborations with two colleagues, and our financial support. We also appreciate the comments from anonymous reviewers which helped to improve this manuscript.
Dr Anna Trykozko from University of Warsaw helped us to validate the software HybGe-Flow3D by running comparisons of permeabilities we obtained with those reported in [46], which were based on flow simulations with ANSYS Fluent.
We also want to thank Dr Masa Prodanovic from The University of Texas at Austin who helped us with the software 3DMA-Rock for pore–network extraction [33].
Funding
This work was partially supported by the grants NSF DMS-1115827 and NSF DMS-1522734. This research was partially supported by the grants NSF DMS-1115827 and NSF DMS-1522734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, T.B., Kennedy, K. & Peszynska, M. Hybrid three-scale model for evolving pore-scale geometries. Comput Geosci 22, 925–950 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-018-9733-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-018-9733-9